TLDR:
-
Historical Evolution of Printing Technology:
- Printing has evolved from ancient woodblock methods to the digital era.
- Early civilisations used woodblocks for stamping patterns and texts.
- Johannes Gutenberg’s movable type printing press revolutionised mass production of books.
- Lithography and offset printing brought further advancements in the 18th and 19th centuries.
-
Basics of Printing Technology:
- Printing involves reproducing text or images systematically onto various surfaces.
- The process allows for mass production and dissemination of information.
- Traditional printing utilises movable type, ink, and presses, while digital printing uses computer-controlled mechanisms.
-
Rise of Digital Printing:
- Digital printing, introduced in the late 20th century, brought efficiency and accessibility.
- Laser and inkjet printers revolutionised printing, offering high-quality prints at remarkable speeds.
- Digital printing opened up new possibilities for various industries and materials, including fabric and metal.
-
Environmental Implications:
- Traditional printing methods consume large amounts of paper, ink, and energy, contributing to deforestation and pollution.
- Sustainable practices, such as recycled paper and eco-friendly inks, are increasingly adopted to minimize environmental impact.
- Digital printing offers benefits like print-on-demand and variable data printing, reducing waste and resource consumption.
-
Future Possibilities:
- Nanotechnology and artificial intelligence are poised to revolutionise printing technology.
- Nanotechnology can enhance precision and efficiency, while AI can optimize processes and quality control.
-
Types of Printing Technology:
- Digital printing utilises inkjet and xerographic technologies for smaller print runs.
- Offset/litho printing is commercially viable for larger print runs, delivering high-quality prints with precise colors and details.
-
Choosing the Best Printing Technology:
- The best printing technology depends on factors like quantity, budget, and desired quality.
- Printulu offers expert guidance and selects the most suitable printing method for each project.
-
Impact of Printing Technology on Industries:
- Printing technology has transformed industries such as retail, education, fashion, and packaging.
- Modern printing methods offer convenience, affordability, and versatility, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
-
Importance of Staying Informed:
- Businesses need to stay updated on printing technology advancements to remain competitive and deliver high-quality products.
- Printulu simplifies the process by selecting the optimal printing method based on project requirements and budget.
-
Advantages of Different Printing Technologies:
- Digital printing offers flexibility, speed, and cost-effectiveness for smaller print runs.
- Offset/litho printing excels in producing high-quality prints for larger quantities, ensuring precise colors and details.
Understanding the basics of printing technology
In order to fully appreciate the advancements in printing technology, it is important to grasp the fundamental concepts behind it. Printing, in simplest terms, involves reproducing text or images systematically onto various surfaces. This process allows for mass production and dissemination of information, making it one of the most significant inventions in human history.
Printing technology has come a long way since its humble beginnings. Let’s take a journey back in time to explore the origins of this remarkable innovation.
The concept of printing: A brief introduction
The concept of printing dates back thousands of years. Early civilisations developed rudimentary methods of stamping patterns onto surfaces using tools such as carved woodblocks. These simple techniques laid the foundation for the printing methods we know today.
One of the earliest known examples of printing can be traced back to ancient China, where woodblock printing was used to reproduce texts and images. This method involved carving characters or designs onto a wooden block, applying ink to the raised surface, and then pressing it onto paper or fabric. The result was a printed impression that could be replicated multiple times.
Over time, printing techniques evolved and spread to other parts of the world. In ancient Egypt, for instance, hieroglyphs were engraved onto stone tablets, allowing for the reproduction of important texts and inscriptions. Similarly, the ancient Greeks and Romans used metal type to create seals and stamps, enabling them to leave their mark on various surfaces.
Key components of traditional printing technology
Traditional printing involves several key components. The printing press, which revolutionised the industry, comprises a frame holding movable type that can be arranged to form words, sentences, and paragraphs. Ink is then applied to the type, which is pressed against paper, transferring the inked impression. This method allowed for faster and more efficient production of printed materials.
During the Renaissance period, Johannes Gutenberg, a German blacksmith and inventor, introduced a groundbreaking innovation that would change the course of printing history forever. In the 15th century, Gutenberg invented the printing press with movable type, a mechanical device that enabled the mass production of books. This invention marked the beginning of a new era, commonly referred to as the “printing revolution.”
Gutenberg’s printing press consisted of a wooden frame, a series of individually cast metal letters, and an inked roller. The letters could be arranged and rearranged to form different words and sentences, making it easier to print multiple copies of a text. This invention not only made books more accessible to the masses but also played a crucial role in the dissemination of knowledge and the spread of ideas during the Renaissance.
As printing technology continued to evolve, new advancements were made in the field. In the 19th century, the introduction of steam-powered printing presses further increased the speed and efficiency of the printing process. This development paved the way for the mass production of newspapers, magazines, and other printed materials, making information more readily available to a wider audience.
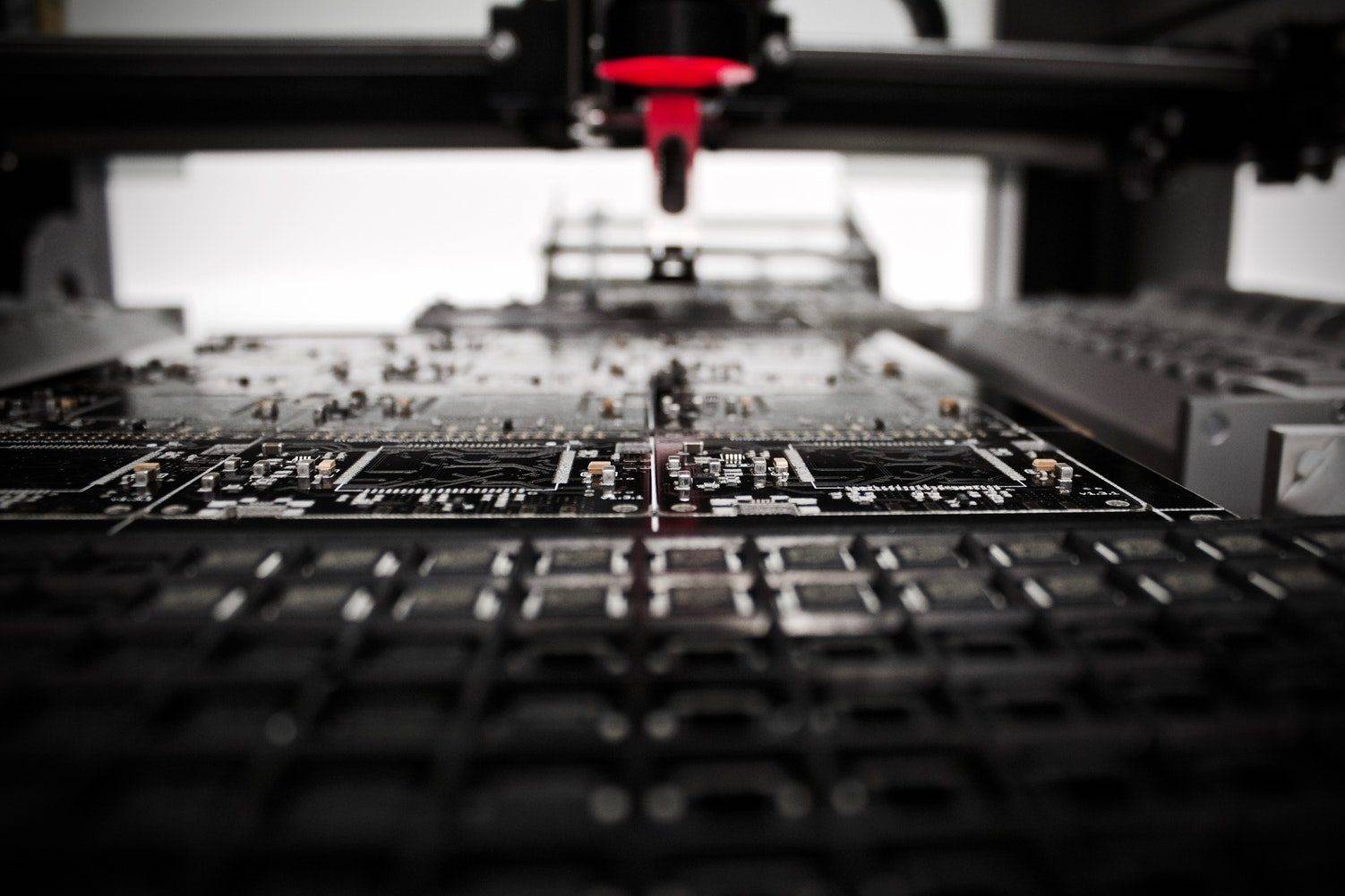
Today, with the advent of digital printing technology, the printing industry has undergone yet another transformation. Digital printers use computer-controlled mechanisms to reproduce text and images, offering greater precision and flexibility. This has opened up new possibilities in fields such as graphic design, advertising, and packaging.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of printing technology allows us to appreciate the remarkable journey it has taken throughout history. From the ancient methods of stamping patterns onto surfaces to the revolutionary invention of the printing press, printing technology has played a vital role in shaping the way we communicate and share information. As technology continues to advance, who knows what the future holds for the world of printing?
Tracing the historical evolution of printing
The historical journey of printing technology began with the innovative methods of early civilisations and progressed through remarkable advancements that shaped the modern world. Let’s take a closer look at the significant milestones along this fascinating path.
The birth of printing: Woodblock and movable type
The earliest form of printing known to mankind is woodblock printing. Ancient Chinese and Egyptian civilisations utilised this method to produce stamps and patterns. The process involved carving out characters or images on a wooden block, which was then inked and pressed onto a surface to create a print. This technique allowed for the replication of simple designs, but it was a time-consuming and labor-intensive process.
However, the true revolution came with the invention of movable type in the 11th century by Bi Sheng in China and later popularised by Johannes Gutenberg in Europe. This breakthrough enabled the printing of entire books with ease and speed, heralding a new era of information dissemination. The movable type involved individual characters or letters made from metal or wood that could be rearranged and reused to create different texts. This innovation revolutionised the printing industry, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
The revolution of the printing press
The invention of the printing press by Gutenberg in the 15th century marked a turning point in the history of printing technology. This ingenious device combined the use of movable type with a mechanical press, allowing for the mass production of books, pamphlets, and newspapers. The spread of knowledge and ideas became more accessible than ever before, triggering significant cultural, social, and scientific advancements.
The printing press not only revolutionised the way information was disseminated but also played a crucial role in the Renaissance and the Reformation. It facilitated the spread of humanist ideas, scientific discoveries, and religious reforms, leading to a profound transformation in European society. The printing press became a powerful tool for challenging authority, fostering intellectual debates, and promoting literacy among the masses.
Lithography and offset printing: A new era
In the 18th century, the development of lithography brought another wave of innovation to the printing industry. This technique, invented by Alois Senefelder, involved using oil and water-based inks on a flat surface, typically a stone or metal plate. The image or text was drawn or transferred onto the surface with a greasy substance, which adhered to the ink and repelled water. When the plate was inked and pressed onto paper, the greasy areas transferred the ink, creating a print.
Lithography revolutionised printing by enabling the reproduction of intricate and detailed images with exceptional clarity and precision. Artists and illustrators embraced this technique, as it allowed them to create high-quality prints of their work. Moreover, lithography opened up new possibilities for commercial printing, such as the production of colourful posters, maps, and advertisements.
Building upon the principles of lithography, offset printing emerged as a dominant method in the early 20th century. In offset printing, the ink is first transferred onto a rubber blanket before being applied to the paper. This indirect printing process offers several advantages, including sharper image reproduction, faster printing speeds, and the ability to use a wider range of materials. Offset printing soon became the preferred method for high-quality commercial printing, catering to various industries such as publishing, advertising, and packaging.
As we delve deeper into the historical evolution of printing, we uncover a rich tapestry of ingenuity, creativity, and technological advancements. From the humble beginnings of woodblock printing to the transformative power of movable type and the printing press, and the refinement of lithography and offset printing, each milestone has left an indelible mark on human civilisation. The continuous evolution of printing technology continues to shape our world, enabling the dissemination of knowledge, fostering cultural exchange, and fuelling innovation.
The rise of digital printing technology
In the late 20th century, the world witnessed the advent of digital printing technology. This revolutionary breakthrough forever changed the landscape of the printing industry.
The introduction of laser and inkjet printers brought unprecedented convenience and efficiency to the printing process. Laser printers use a laser beam to transfer toner onto the paper, producing high-quality prints at remarkable speed. Inkjet printers, on the other hand, use tiny droplets of ink sprayed onto the paper, allowing for vibrant colours and intricate detail. These advancements made printing accessible to individuals and small businesses, empowering them with the ability to create professional-quality prints from their own homes or offices.
But let’s delve deeper into the fascinating history of digital printing technology. The concept of digital printing can be traced back to the early 1950s when the first computer-driven printer was developed. This early printer, known as the IBM 3800, used a laser beam to create images on paper. However, it was not until the late 1980s that digital printing truly took off with the introduction of the first commercial inkjet printer.
As digital printing technology continued to evolve, so did its applications. In addition to producing high-quality prints, digital printers also became capable of handling a wide range of materials, including fabric, plastic, and even metal. This opened up a whole new world of possibilities for industries such as fashion, packaging, and signage.
The impact of 3D printing technology
One of the most exciting advancements in recent years is the rise of 3D printing technology. Also known as additive manufacturing, this process involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer using a computer-controlled printer. From prototyping to customized manufacturing, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionise various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, and design.
But how exactly does 3D printing work? Well, it all starts with a digital model of the object you want to create. This model is then sliced into thin layers, and the 3D printer uses this information to build the object layer by layer. The printer deposits material, such as plastic or metal, in precise locations, gradually building up the final product.
3D printing has already made significant strides in various fields. In the aerospace industry, for example, 3D printing has been used to create complex components that are lighter and more efficient than traditional manufacturing methods. In healthcare, 3D printing has enabled the production of customized prosthetics and implants, improving the quality of life for many individuals.
Looking ahead, the potential of 3D printing seems limitless. Researchers are exploring the possibility of using 3D printers to create human organs, revolutionising the field of organ transplantation. Additionally, architects and designers are experimenting with 3D printing to create intricate and sustainable structures, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in construction.
As we reflect on the rise of digital printing technology, it becomes clear that this innovation has not only transformed the printing industry but also opened up new avenues for creativity and innovation. From the convenience of home printing to the limitless possibilities of 3D printing, the future of printing technology is undoubtedly bright and full of exciting possibilities.
When it comes to new printing technology, the industry is constantly evolving to meet the demands of businesses and consumers alike. From 3D printing to digital printing advancements, the options are vast and ever-changing. Keeping up with the latest developments in printing technology is crucial for businesses looking to stay ahead of the competition and deliver high-quality products to their customers. Whether it’s exploring eco-friendly printing options or investing in cutting-edge machinery, staying informed about new printing technology can make a significant impact on your business’s success.
The environmental implications of printing technology
While the evolution of printing technology has brought immense benefits, it is essential to consider its environmental impact.
Printing technology has revolutionised the way we communicate and share information. From the early days of Gutenberg’s printing press to the modern digital printers, printing has become an integral part of our daily lives. However, the convenience and efficiency of printing come at a cost, and it is crucial to understand the environmental implications.
The ecological footprint of traditional printing
Traditional printing methods typically involve the use of large amounts of paper, ink, and energy. This results in the consumption of valuable resources and contributes to deforestation, pollution, and waste. The demand for paper in the printing industry has led to the destruction of countless trees, leading to habitat loss and a decline in biodiversity.
Moreover, the production of ink requires the extraction of raw materials, such as petroleum and chemicals, which have detrimental effects on the environment. The manufacturing process of ink releases harmful emissions and pollutants into the air and water, contributing to air pollution and water contamination.
In addition to the use of resources, traditional printing methods also generate a significant amount of waste. Misprints, outdated materials, and excess inventory contribute to landfill waste, further exacerbating the environmental impact.
However, efforts are being made to minimise these impacts through sustainable practices. The printing industry is increasingly adopting environmentally friendly alternatives to reduce its ecological footprint.
Sustainable practices in modern printing technology
Modern printing technology has introduced greener alternatives to minimise its environmental impact. The adoption of recycled paper is one such practice that has gained popularity. By using recycled paper, the demand for new paper production is reduced, leading to a decrease in deforestation and habitat destruction.
Eco-friendly inks have also emerged as a sustainable choice in printing. These inks are made from natural and renewable resources, such as vegetable oils and soy. Unlike traditional petroleum-based inks, eco-friendly inks have a lower environmental impact and produce fewer harmful emissions.
Furthermore, energy-efficient printing presses have become a standard in the industry. These presses are designed to consume less energy while maintaining high-quality printing. By reducing energy consumption, the carbon footprint of the printing process is significantly reduced.
Another sustainable practice in modern printing technology is the adoption of digital printing. Unlike traditional offset printing, digital printing allows for print-on-demand capabilities, eliminating the need for large print runs and excess inventory. This not only reduces waste but also saves resources and energy.
Moreover, digital printing offers the option of variable data printing, enabling personalised printing on a mass scale. This targeted approach reduces the need for excessive printing and minimises the amount of paper and ink used.
While sustainable practices in printing technology have made significant progress, there is still room for improvement. Continued research and innovation are necessary to develop even more environmentally friendly printing methods.
In conclusion, the environmental implications of printing technology cannot be ignored. However, through the adoption of sustainable practices and the continuous development of greener alternatives, the printing industry is striving to reduce its ecological footprint. By making conscious choices in printing, we can contribute to a more sustainable future.
The future of printing technology
As we continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the future holds exciting possibilities for printing technology.
The potential of nanotechnology in printing
Nanotechnology has emerged as a promising field with the potential to revolutionise the printing industry. By manipulating materials at the molecular level, printing could reach new heights of precision and efficiency. The integration of nanotechnology into printing processes can lead to breakthroughs in areas such as electronics, biomedicine, and renewable energy.
The role of artificial intelligence in future printing
Artificial intelligence (AI) is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of printing technology. AI-powered software can enhance printing processes, optimise resource utilisation, and improve quality control. Machine learning algorithms can analyse data, automate repetitive tasks, and enable intelligent decision-making, leading to greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
In conclusion, the evolution of printing technology has been a journey of ingenuity, innovation, and transformation. From the humble beginnings of woodblock printing to the era of digital printing and beyond, printing technology has continually evolved to meet the growing demands of society. The future promises even greater advancements, with nanotechnology and artificial intelligence poised to redefine the printing landscape. As the world becomes increasingly digital, printing technology continues to shape and influence our lives, allowing us to share knowledge and ideas in once unimaginable ways.
Printing is arguably one of the most important cornerstones of our civilisation. It has revolutionised multiple industries and has become an important fundamental practice of society. Printing technology itself has also seen enormous progress with the emergence of the retail revolution and growing education globally.
Printing is no longer dependent on laborious processes but has evolved into something that can be done at the click of a button at your home. It has even become possible to print 10,000 sheets of paper per hour, and it has become increasingly easier to print on materials other than paper, such as polyester and E-Flute.
Today products such as selfie-frames, entry form boxes (also known as ballot boxes), paper bags, and even wallpaper for your home can be printed at the touch of a button! Don’t believe us?
It is even possible to decorate an entire store with printed materials at a comparatively low cost, right down to the contravision sticker that draws customers to your store front.
One of the immense developments we’ve seen in the printing business are the innovations in printing technology that gave rise to digital printing. Digital printing has dominated the printing market because of its comparatively lower cost, faster printing time and ability to print small runs.
What is Digital Printing?
Digital printing is a revolutionary printing method that transfers ink directly onto a range of media. In comparison to offset printing, digital printing doesn’t utilise plates to print or transfer an image. Digital printing makes use of toners, making it an economical printing method for lower-quantity print orders.
There are two main printing technologies that are used with digital printing:
- Inkjet – With an inkjet printer, the print is created by small droplets of ink that are propelled from the nozzles of the print heads. These printers can print on a wide range of materials, such as paper, plastic, and even canvas. Inkjet printing is mainly used for posters and signage. In-line inkjet printers are also sometimes combined with other types of printing presses to print variable data. (See: Variable Data Printing – How to Personalise Your Print Marketing)
- Xerography – Xerographic printers are a range of printers that includes, among others, laser printers. This technology forms the print by selectively applying a charge to a metal cylinder called a drum. This electrical charge is used to attract toner particles. These particles are then transferred to the media that is being printed. To make sure the toner is fixed properly, the print passes through a fuser that melts the toner into the medium. Laser printing is commonly used in offices as well as for small runs such as brochures and other types of documents.
Offset/Litho Printing – For Larger Runs
Capable of producing up to twenty kilometres of printed media in just one hour, offset printing is much more commercially viable than printing technologies designed for smaller print runs. Offset or litho printing is a printing technique wherein the inked image is “offset” or transferred from a plate, commonly crafted from aluminium, onto a blanket made out of rubber and then rolled on a sheet of paper. It operates on a simple principle: oil-based ink and water don’t mix.
The image that needs to be printed is put on thin metal plates which are dampened by water and ink. This is done with rollers on the press. The oil-based ink adheres to the image areas, whilst the water adheres to the non-image areas. The inked area is then transferred to a rubber cylinder or “blanket” and then onto the paper as it passes around the blanket. The process is called “offset” because the ink isn’t transferred directly from the printer onto the paper.
This printing technique delivers and prints clean and precise colours and is great for large-quantity prints. Offset printing produces rich, accurate colour and high-quality images and photographs, with sharp typefaces and fine details. When you need 250 to 500 or more business cards, postcards, posters, glossy brochures, flyers or catalogues, offset printing is tough to beat for high-end quality at an affordable price.
What is the Best Type of Modern Printing Technology for You?
Are you planning on printing new customer signage, posters, or other printed media? If so, it might make sense to reach out to a printing company directly, since this decision can ultimately have an impact on the overall costs associated with the printing job.
Luckily, when printing with Printulu, you can skip all of that hassle. We make the decision for you based on years of experience in the industry and expert knowledge of what will suit your specific project and budget best. When you place your order with Printulu, the price already includes the best possible printing method that we will use for you. So sit back, relax, and rest assured that your printed products will be delivered to you in no time at top quality.